To save the planet, first save elephants
Wiping out all of Africa’s elephants could accelerate Earth’s climate crisis by allowing 7% more damaging greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, scientists say. But conserving forest elephants may reverse
Wiping out all of Africa’s elephants could accelerate Earth’s climate crisis by allowing 7% more damaging greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, scientists say. But conserving forest elephants may reverse
The Arctic continues to amaze. Hit by a second bout of extremely warm winter temperatures in recent days, the seasonal growth of floating sea ice has flattened out, just as it did when hit by similarly
Engineers from The Ohio State University have found a way to convert heat into electricity by applying their technique to capture "waste heat," the byproduct of electrical and mechanical devices like car
Researchers in the United States have found that local experiences and temperatures drive belief or non-belief of people in climate change. The study, published in the Journal of Proceedings of the National

Scientists have developed a new technology that uses nuclear waste to generate clean electricity in a nuclear-powered battery. Researchers from the University of Bristol in the UK have grown a man-made
A new study reveals that air pollution has found to have traces of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which cannot be treated by common antibiotics. Scientists warned that these bacteria are causing some viruses
After decades of battling the growing number of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) infections across the globe, a new major HIV vaccine trial is set to start in South Africa. This historic trial promises
Scientists have discovered that the transport of Sahara Desert dust in the atmosphere may have crucially affected the changes in climate for thousands of years. The presence of dust in air and settling
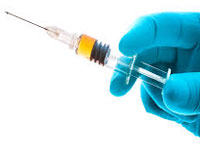
Scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) in the US have developed a vaccine that appears to decrease the risk of fatal opioid overdose. The vaccine blocks the pain-numbing effects of the

Scientists think the leopard could have come to Delhi from Kalesar in Haryana, 400 km from the city, which has a healthy population of leopards. The spotting of a leopard at the Yamuna Biodiversity

The rising warm air, in turn, sucks in cooler air from Indian Ocean, causing an earlier onset of monsoon Pollutants from China and India, are not only increasing in quantity but are also being pumped