12 billion years
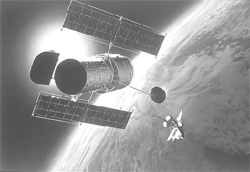 the Hubble Space Telescope Key Project team has announced that its efforts to measure the distances of far-away galaxies are now complete. To achieve this, the eight-year effort has been using the Hubble space telescope ( hst ). This, in turn, is an essential ingredient for determining the characteristics of the universe like its age, size and even its ultimate fate. The team estimates the universe to be approximately 12 billion years old.
the Hubble Space Telescope Key Project team has announced that its efforts to measure the distances of far-away galaxies are now complete. To achieve this, the eight-year effort has been using the Hubble space telescope ( hst ). This, in turn, is an essential ingredient for determining the characteristics of the universe like its age, size and even its ultimate fate. The team estimates the universe to be approximately 12 billion years old.
One of the essential measurements in astronomy is the rate of expansion of our universe. According to the current theory, the universe started with a cataclysmic event known as the Big Bang. The universe has been expanding since. The objects in the universe are all moving away from each other. The rate of this expansion is known as the Hubble constant after Edwin Hubble, who in 1929 was the first to discover that the galaxies were receding from each other. The measurement of the Hubble constant can tell us how fast two galaxies are moving away from each other.
Only it is not as easy as that
Related Content
- Reducing post-harvest losses in India: farmer-level interventions and grain management strategies
- 2023 disasters in numbers
- Reducing post-harvest losses in Indian agriculture: a case study of selected crops
- Natural catastrophes in 2023: gearing up for today’s and tomorrow’s weather risks
- The global e-waste monitor 2024
- Profits and poverty: the economics of forced labour
