The global e-waste monitor 2024
<p>The world's electronic waste generation is increasing five times faster than documented e-waste recycling, according to the United Nation's fourth Global E-waste Monitor (GEM) report.</p>
<p>The world's electronic waste generation is increasing five times faster than documented e-waste recycling, according to the United Nation's fourth Global E-waste Monitor (GEM) report.</p>
DH News Service, Bangalore: In the latest Greenpeace Guide to Greener Electronics, Nokia bounced back to the first position in the ninth international edition as well as topped the fourth Indian edition amongst the MNCs here. Which are the brands close to going green? Do they have in place a take back practice? Do they support the legislation on the Restriction of the Use of Certain Hazardous Substances in Electrical and Electronic Equipment or RoHS? Do they manufacture clean or toxic free products?
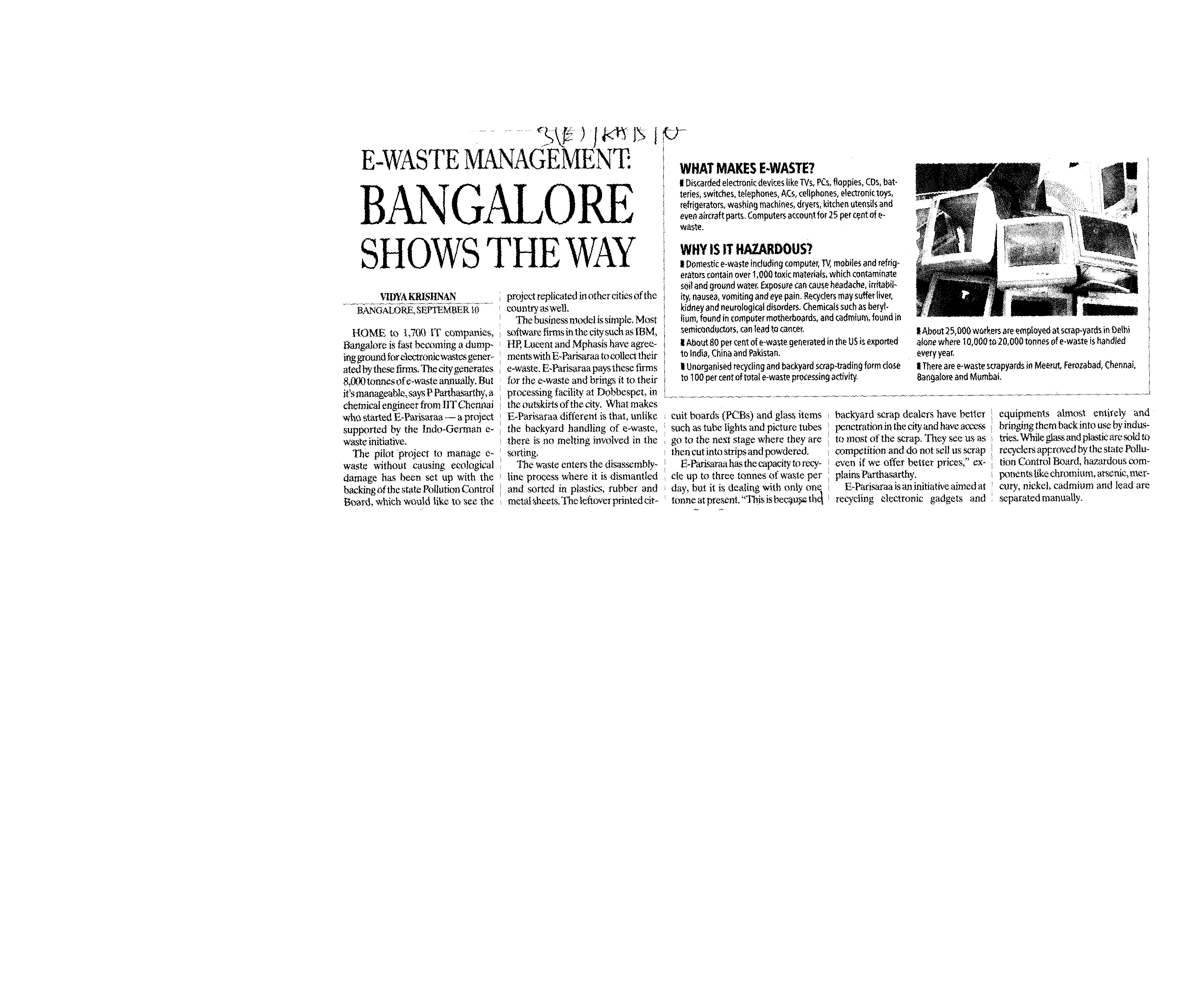
Bangalore shows the way. Home to 1,700 IT companies, Bangalore is fast becoming a dumping ground for electronic wastes generated by these firms. Please see the attachment for the full news...
By Shruti Badyal
The information and communication technology (ICT) sector in the last twenty years or so in India has revolutionized life of one and all, ratcheting a viral effect on electronic manufacturing industries leading to phenomenal growth in terms of both, volume and applications. Digital development has become the new mantra having its all engulfing footprints every where. The report focuses only on the policies and practices of electronic brands on the Indian market.
Mumbai, July 24 A training on e-waste for members of several urban municipal corporations from the western region on Thursday turned into a brainstorming session of sorts when the civic officials highlighted their difficulties in handling not just electronic wastes but also bio-medical wastes in their cities due to absence of proper regulation.
Pune June 29 The Pune Municipal Corporation (PMC) has expressed concern over the poor response from the information technology (IT) companies to address the problem of electronic waste being generated in the city despite efforts made by the civic body. "The PMC has initiated steps to tackle the e-waste problem, but there is not much response from the IT companies," Ajay Ojha, PMC Environment Cell, in-charge, said at a meeting with representatives of 200 IT companies organised recently by city-based NGO Sarathi.
Mumbai, June 29 With the city topping the list in generating the highest amount of electronic waste in the country, the Mumbai Metropolitan Region Development Authority (MMRDA) along with the Maharashtra Pollution Control Board (MPCB) will soon be searching for a landfill site exclusive to treat and dump e-waste as a pilot project.
Noble metals and Cu mainly are recycled in treating waste printed circuit boards (PCBs), and a large amount of nonmetallic materials in PCBs are disposed of by combustion or landfill, which may cause secondary pollution and resource-wasting. In this study, a kind of nonmetallic plate (NMP) has been produced by nonmetallic materials of pulverized waste PCBs. The NMP is produced by a self-made hot-press former through adding resin paste as a bonding agent.
* Air pollution in India causes 5,27,700 deaths every year (WHO) * 21% of communicable diseases in India are related to polluted water. In India, diarrhoea alone causes more than 1,600 deaths daily (WHO) * Only 22% of the wastewater generated in urban India is treated, severely polluting rivers. The total wastewater from Delhi and nearby areas flowing into the 19 drains that connect to the Yamuna is around 3,296 million litres a day, of which 630 MLD is untreated.
In order to check proliferating hazardous e-waste recycling units in the national capital, Delhi Government is roping in private sector to regulate the process. "We have asked the private sector to come forward to develop an electronics waste management project on the basis of public-private partnership,' Delhi Environment Secretary JK Dadoo told PTI here. Delhi is emerging as the world's capital for e-waste recycling, a hazardous activity taking place without any regulations with the major dismantling taking place in unorganisedinformal sector.