African merchandise
 • Of the 38 countries in Africa, the percentage of people living with low sustainability has gone up from 34.1 per cent in 1975-84 to 54 per cent in 1995-2000
• Of the 38 countries in Africa, the percentage of people living with low sustainability has gone up from 34.1 per cent in 1975-84 to 54 per cent in 1995-2000
• Only three countries, accounting for 6.5 per cent of the continent's population, have recorded relatively high overall sustainability during this period
• Environmental sustainability has gone down in Africa considerably, with a brief recovery during 1996-2000
• Africa contributes just two to three per cent of the world's carbon dioxide emission from industrial and energy sources, but suffers more from climate change, resulting in more droughts, floods and cyclones
• Its wilderness will vanish in the next 50-100 years, as climate change will make it impossible for wild organisms to survive in this continent
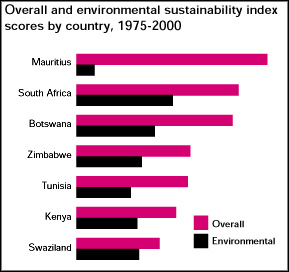
• The top five countries in the overall sustainability list are also the worst performers in the environmental sustainability index. Mauritius, which has the highest overall sustainability, is the last in the environmental sustainability list
• Africa carries the highest disease burden in the world. An unprecedented 30 per cent of this burden is due to environment-related diseases like malaria and respiratory infections
• Its ecology naturally supports infectious diseases, but the lack of access to sanitation, medical care and the rising poverty levels compound the problem
• Africa's high burden of disease has already slowed down its demographic transition
• In several countries, HIV/AIDS has reduced life expectancy by more than 10 years. Life expectancy will never rise above 55 years due to bad health services
• Among the top five countries in the overall sustainability rankings, average life expectancy has declined by about three years between 1985-94 and 1995-2000. Among these countries, Botswana, South Africa and Zimbabwe are worst affected by HIV/AIDS
SOURCE: Harnessing Technologies for Sustainable Development, Economic Commission for Africa (ECA), ECA Policy Research Report, Addis Ababa, 2002
| Burden of disease from major environmental risks (percentage of disability-adjusted life years lost in each group) | |||
| Environmental risk | Africa | Asia and Pacific | Latin America |
| Urban air pollution | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Malaria | 9 | 1.5 | 0 |
| Agro-industrial waste | 1 | 1.5 | 2 |
| Indoor air pollution | 5.5 | 4 | 0.5 |
| Water supply and sanitation | 13 | 10 | 7 |
| Total | 29.5 | 19 | 12.5 |
| Source: Lvovsky and others 2000; Lvovsky 2001 | |||
