Biodiversity Asia
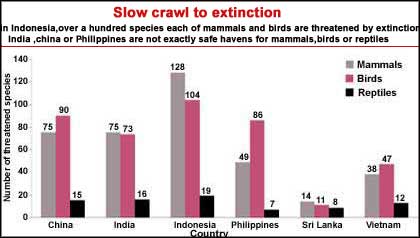 Asian floral and faunal species are threatened by fragmentation, physical alteration, habitat loss, pollution, introduction of exotic species and overexploitation of ecosystems. About 20 per cent of world's freshwater fish species have become extinct, many of them endemic to Asia. Be it mammals, birds or reptiles, they all suffer a similar fate. In Indonesia, nearly one-fourth of mammals are classified as threatened. Plant species fare no better. In India more than 700 higher plant species are threatened. Large populations in Asian countries directly depend on natural resources like forests and fisheries. Their fate, too, hangs in the balance.
Asian floral and faunal species are threatened by fragmentation, physical alteration, habitat loss, pollution, introduction of exotic species and overexploitation of ecosystems. About 20 per cent of world's freshwater fish species have become extinct, many of them endemic to Asia. Be it mammals, birds or reptiles, they all suffer a similar fate. In Indonesia, nearly one-fourth of mammals are classified as threatened. Plant species fare no better. In India more than 700 higher plant species are threatened. Large populations in Asian countries directly depend on natural resources like forests and fisheries. Their fate, too, hangs in the balance.
Related Content
- State of the world’s migratory species
- Living in the shadow of loss and damage: uncovering non-economic impacts
- Insurance to promote human-wildlife coexistence
- Water, ice, society, and ecosystems in the Hindu Kush Himalaya: an outlook
- An assessment of wildlife trade between Madagascar and Southeast Asia
- Implementation of the Convention on Biological Diversity in the Hindu Kush Himalayan countries: a retrospective analysis of Aichi Targets
