Poverty perspective
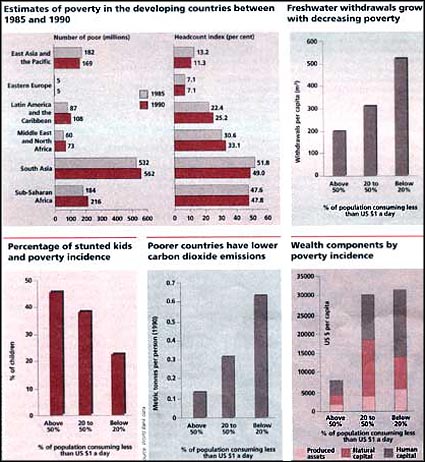 Reduction of poverty remains one of the foremost global challenges. An estimated 1.3 billion persons in the developing world will live in. absolute poverty by the turn of the century. While the Headcount method of measuring poverty counts the proportion of people whose income or consumption is below a certain minimum level, the Poverty gap measures the extent of this shortfall Use of major resources are related directly to poverty incidence: the use of freshwater goes up as poverty decreases, as does nutrition and health behaviour. As one graph shows, sharp changes occur in the wealth cpmponent by poverty incidence. Thus, a global strategy for poverty eradication must be informed with environmental considerations to promote sustainable development
Reduction of poverty remains one of the foremost global challenges. An estimated 1.3 billion persons in the developing world will live in. absolute poverty by the turn of the century. While the Headcount method of measuring poverty counts the proportion of people whose income or consumption is below a certain minimum level, the Poverty gap measures the extent of this shortfall Use of major resources are related directly to poverty incidence: the use of freshwater goes up as poverty decreases, as does nutrition and health behaviour. As one graph shows, sharp changes occur in the wealth cpmponent by poverty incidence. Thus, a global strategy for poverty eradication must be informed with environmental considerations to promote sustainable development
Related Content
- Accelerating an equitable transition: a framework for economic equity
- Multidimensional poverty in India since 2005-06
- National multidimensional poverty index: a progress review 2023
- Leaving no one behind: rethinking energy access programs in displacement settings
- Suitable MGNREGS practices and convergence opportunities for regional development priorities: a compendium
- Forest products in the global bioeconomy: enabling substitution with wood-based products and contributing to sustainable development goals
