State of India’s digital economy report 2023
The State of India’s Digital Economy (SIDE) Report measures and analyses India’s digital transformation using data, information and evidence that are specifically relevant to the Indian context. In this,
The State of India’s Digital Economy (SIDE) Report measures and analyses India’s digital transformation using data, information and evidence that are specifically relevant to the Indian context. In this,
Old handsets have a knack of getting handed down, rarely discarded. According to the results of a global consumer survey, conducted by Nokia on 6,500 people in 13 countries as far-flung as Germany, the UAE, USA, Nigeria, India and China, only 3 per cent of people recycle their
1-0 binary data transmission may change for the better
A penny saved is a penny earned. That is a maxim that telecom operators worldwide appear to have adopted as a motto. While that is not unusual, what is heartening is that they are looking at saving on energy costs through renewable energy sources and better equipment.
TELECOM AND NETWORK CONNECTIVITY have widely been seen as enablers of a nation's socio-economic growth; a McKinsey study cites that a 10 per cent increase in teledensity contributes to 0.6 per cent of GDP growth. Though urban India is reaping the benefits of the telecom revolution, rural teledensity is still low, at only 8 per cent.
The Eleventh Five Year Plan has set an ambitious target of increasing total investment in infrastructure from around 5% of GDP in the base year of the Plan 2006-07 to 9% by the terminal year 2011-2012.

Mobile phone industry thwarts radiation guidelines India has adopted the limits on electromagnetic radiation from mobile phones and base stations set by the International Commission for Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (icnirp), but still not adopted guidelines for regulation. According to an official in the Department of Telecommunications, the delay is because the telecom industry
Tower Power density is power per unit area. ICNIRP guidelines set density limits for occupational exposure and the public. For the public using GSM mobiles the limit has been kept at 4.5 W/sq m for 900 MHz and 9 W/sq m for 1,800 MHz. For CDMA phones it is 4W/sq m. Occupational exposure limits are five times the public limits. Mobiles Strength of the mobile signal determines the
Mobile phones, like radios, rely on radio frequencies to communicate. They operate at 800, 900 and 1,800 MHz, which are also referred to as microwaves. In the electromagnetic spectrum they fall between radiowaves and infrared rays. Mobile phones
This document presents a simple approach to elaborate a scenario regarding the potential impacts of a tsunami in a city exposed to such a hazard. The approach has been tailored to span eleven typical development sectorswhich are present in every city such as health,education,housing, life-lines, transportation, telecommunications, industry, government, etc.
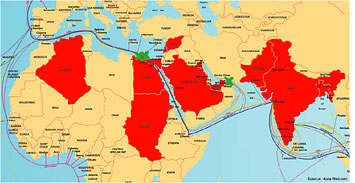
Work has begun to repair three damaged undersea fibre-optic cables that were severed in the Mediterranean Sea and the Persian Gulf on January 30 and February 1. The cause of the cable break is